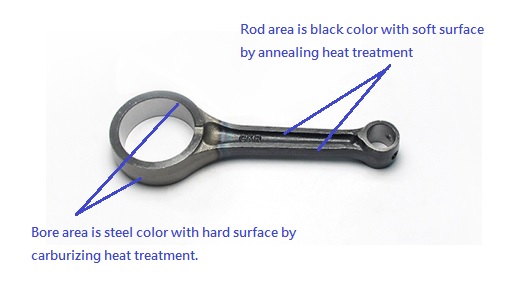
A connecting rod is an engine part that connects a piston to a crankshaft in an internal combustion engine. For motorcycle engines, a high strength connecting rod is required to bear the combustion forces from the piston and transfer them to rotational torques to the crankshaft. Forged connecting rods, made of chromoly steel, are manufactured through a series of processes including hot forging, rough machining of planes and bores, heat treatment, and precise grinding of planes and bores.

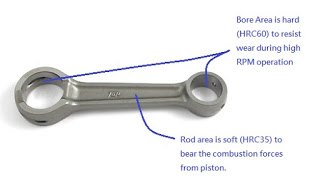
A motorcycle connecting rod is especially important in motorcycle engines because the bore race has to be hard (HRC60) to resist abrasion from the crank pin and piston pin during high RPM operation. However, a hard material is brittle, which may cause connecting rod failure in the rod area. To avoid connecting rod breaking, the hardness in the rod area must be lowered to HRC35. This makes the material at the rod area more ductile, allowing the motorcycle engine to operate safely with a good connecting rod.
Another important specification of a connecting rod is the roundness of the connecting rod bore. Roundness measures how closely the bore approaches a perfect circle. The bore diameter is measured at different angles, and roundness is the difference between the maximum and minimum of all the diameter measures. Generally, a qualified motorcycle connecting rod requires a roundness of 0.003mm for both the big-end bore and small-end bore. Therefore, achieving perfect bore roundness ensures the engine operates smoothly and greatly enhances the durability of the connecting rod.